Whisky is a spirit with a large historical and cultural significance, with many people having flown its flag to make it the globally known spirit it is today. Its history and origin, however, are muddied and up for debate (the whisky itself probably did not help either). Both the Scots and the Irish claim to be the inventors of it, but there is insufficient evidence to favour either party in the debate.
Whisky/Whiskey comes from the old Gaelic ‘uisge beatha’, or ‘usquebaugh’, meaning ‘water of life’, similar to the Scandinavian ‘aquavitae’. While there is some evidence suggesting the technique of distillation was brought over to the British Isles by Christian missionary monks, it is insufficient to disprove that Scottish or Irish farmers did not discover the technique of distillation themselves. However, the oldest evidence of distillation we have can be traced back to as far as 2000 B.C. in ancient Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq and Syria) as a way to produce perfumes and aromatisers. Hence, it is more than likely the former is the case, and lacking the climate for vineyards, opted to ferment grain, leading to the first versions of what we now know as whisky.
While we are unsure who made this wonderful liquid first, there are key differences between Scotch and Irish whiskies, from their raw materials to distillation and maturation.
Irish v Scottish
The Scots and Irish also produce many blended whiskies, a mix of multiple liquids, from multiple distilleries (malt, grain, and rye whiskies all included!) within the same geographical region. These liquids are masterfully selected by a master blender and proportioned expertly to produce a whisky that is greater than the sum of its parts.
A few years ago, I had the privilege of having Emma Walker, master blender of her namesake Johnnie Walker, perch up at the bar of the prep room while I was working a prep shift. This allowed me unfiltered access to one of the greatest minds in the modern whisky world and she (to my benefit) oversimplified what she does for work and explained it as:
“Not too dissimilar to making a cocktail. The same way you would balance a cocktail behind a bar using spirits, liqueurs, juices, and syrups. In the blending room we take the same approach, the only difference is we are tasked with balancing whisky with, well, more whisky.”
Blended Scotch Whiskey - Johnnie Walker Black Label
Size: 700ml
ABV: 40%
Find here: £24.99
Blended Irish Whiskey -Tullamore D.E.W.
Size: 700ml
ABV: 40%
Find here: £24.64
The United States
As British colonisers started to land and settle in the Americas, specifically Kentucky, they realised the climate in the Southeast area of the United States was not conducive to the cultivation of barley. To work around this, they started distilling whiskey from corn, which later became known as the bourbon we know and love today.
Bourbon must be made in the United States using at least 51% corn in the mash bill. To be considered bourbon, it must also be distilled to no more than 80% ABV, bottled at a minimum of 40% ABV, and aged in charred virgin oak barrels with no minimum maturation period. However, to be considered “straight bourbon”, it must be aged for a minimum of two years.
Rye Whiskey has very similar production process specifications to Bourbon, with the same requirement of at least 51% Rye in the mash bill to be considered as such. The key difference in flavours, comes from the raw materials used in the production process. Bourbon tends to be more full-bodied and sweeter, while Ryes are generally drier, spicier, and have an underlying bready note.
There is also Tennessee whiskey, which is akin to bourbon in many of its processes, to the point where most Tenessee whiskies meet the requirements for bourbon. The key difference is that all Tennessee whiskies must be filtered using the Lincoln County Process which entails filtering (or steeping) the new-make spirit in charcoal chips before aging. However, many producers do not label themselves as such and prefer to label their products as Tennessee Whiskey.
Rye Whiskey - Rittenhouse Straight Rye
Size: 700ml
ABV: 50%
Find here: £39.99
Bourbon Whiskey - Buffalo Trace Bourbon
Size: 700ml
ABV: 40%
Find here: £26.68
Tennessee Whiskey - Daddy Rack Straight Tennessee Whiskey
Size: 700ml
ABV: 40%
Find here: £39.99
Canada
Canadian whisky later joined the party as American and European immigrants used their experience in distilling wheat and rye to preserve surplus grain in attempts to prevent spoilage. This was done in improvised stills and resulted in inconsistent, and uncontrolled new-make spirits, drank unaged by the local market. Commercial whisky production in Canada started when John Molson purchased a copper pot still initially used to distill rum.
Canadian whisky has the most relaxed controls in the world of whisky as the regulations lack any strict stipulations in terms of mash bill content and additives. As per Canada’s Food and Drugs Act, to be called Canadian whisky the liquid must "be mashed, distilled and aged in Canada", "be aged in small wood vessels for not less than three years", "contain not less than 40 percent alcohol by volume" and "may contain caramel and flavouring". However, distillers must not veer too far away from the original form as the liquid must "possess the aroma, taste and character generally attributed to Canadian whisky."
Canadian Whiskey - Lot 40 Rye Whisky
Size: 700ml
ABV: 43%
Find here: £37.99
Japan
The advent of Japanese whisky can be attributed to two main characters, Shinjiro Torii and Masataka Taketsuru. Torii was a pharmaceutical wholesaler by trade who made a profit by importing Western world liquor with his company “Akadama Port Wine”, named after the Portuguese fortified wine. Torii then set his sights on creating a Japanese whisky to rival that made in Scotland, Ireland, and the United States, and opened the distillery which would later be known as Yamazaki.
Torii hired Taketsuru, who had honed the art of making whisky in Scotland and used this knowledge to help establish the Yamazaki distillery as a successful one, before parting ways with the company in 1934 to start his own company Dainipponkaju, which would later become Nikka.
The influence these two people had on Japanese whisky resulted in it being the closest thing to Scotch whisky you can get outside Scotland. With very similar legal requirements to its Scottish counterpart, the key flavour differences come from the two countries' environmental differences.
Japanese Single Malt Whisky - Yamazaki 12 YO
Size: 700ml
ABV: 43%
Find here: £139.95
Japanese Blended Whisky - Toki Blended
Size: 700ml
ABV: 43%
Find here: £31.89
New World Whiskies
As whisky is currently enjoying another moment in the spotlight, new kids on the block, from different corners of the globe, are looking to stamp their mark on the whisk(e)y industry. Notably, these include Taiwan, France, Germany, Australia, and China, but as of 2022, over 30 countries are producing new world whiskies.
French - Domaine des Hautes Glaces Epistémè
Size: 500ml
ABV: 47%
Find here: £72.24
Chinese - Goalong 5 YO
Size: 700ml
ABV: 40%
Find here: £52.95
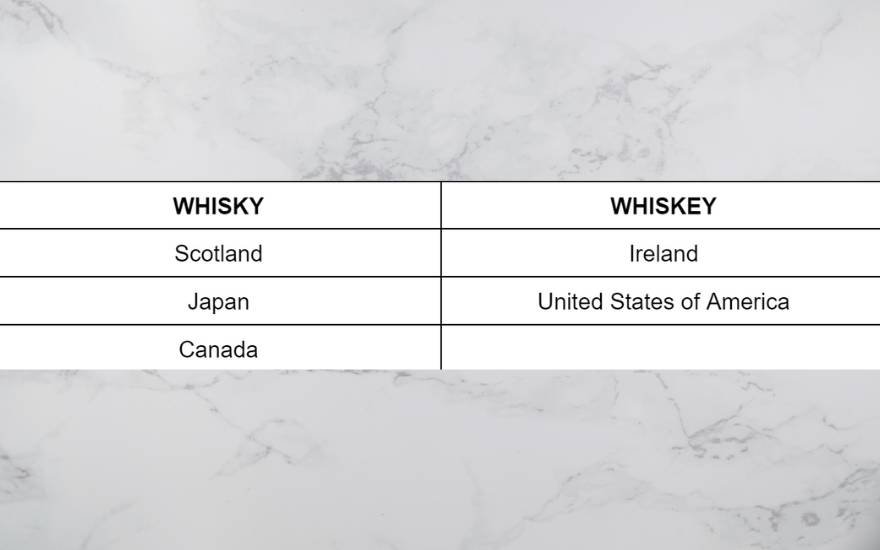
Ultimately, the choice of spelling it as whisky or whiskey boils down to traditional use and does not depict any discrepancies in raw materials, production process, or flavours. Scotland, Japan, and Canada all make whisky that tastes remarkably different from one another, within the United States of America alone there are three variations of whiskey with unique processes and flavour profiles.
By Fowwaz Ansari